Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is one of the significant health concerns that affect millions of women worldwide. Despite advances in screening and prevention, it remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women, particularly in developing countries where access to healthcare services is limited. In this blog post, we will explore the intricacies of cervical cancer, including its causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies.
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer grows in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that links to the vagina. The human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection, is the primary cause of cervical malignancies. However, not all women infected with HPV will develop cervical cancer, indicating that other factors play a role in its development.
Causes of Cervical Cancer:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those living with HIV/AIDS or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are at higher risk of developing cervical cancer.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains carcinogens that can damage cervical cells, increasing the risk of cervical cancer.
- Early Sexual Activity: Engaging in sexual activity at a young age increases the likelihood of HPV infection, which is a significant risk factor for cervical cancer.
- Multiple Sexual Partners: Having multiple sexual partners or engaging in sexual activity with someone who has had multiple partners increases the risk of HPV transmission and subsequent cervical cancer.
- Long-Term Use of Oral Contraceptives: Some studies suggest that long-term use of oral contraceptives may slightly increase the risk of cervical cancer.
- Poor Socioeconomic Conditions: Factors such as limited access to healthcare, lack of education about cervical cancer screening and prevention, and inadequate resources for early detection and treatment contribute to higher cervical cancer rates in certain populations.
- Family History: While cervical cancer is not considered a hereditary disease, having a family history of cervical cancer or certain genetic mutations may slightly increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Diet and Nutrition: A diet low in fruits and vegetables and high in processed foods may contribute to an increased risk of cervical cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand the impact of diet on cervical cancer risk.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer:
In its early stages, cervical cancer may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, with the advancements of the stages most of the women may experience some the following symptoms:
1. Abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding between periods, after intercourse, or after menopause.
2. Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse.
3. Unusual vaginal discharge that may be watery, bloody, or foul smelling.
It is essential to note that these symptoms can also be caused by conditions other than cervical cancer. Nevertheless, any persistent or unusual symptoms should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider for evaluation.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer:
1. HPV Vaccination: Vaccination against HPV is the most effective way to prevent cervical cancer. The HPV vaccine is recommended for both boys and girls, ideally, before they become sexually active.
2. Routine Screening: Regular cervical cancer screening, typically done through Pap tests or HPV tests, can detect precancerous changes in the cervix early, allowing for timely intervention.
3. Safe Sexual Practices: Practicing safe sex, such as using condoms and limiting sexual partners, can reduce the risk of HPV infection and cervical cancer.
4. Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can lower the risk of developing cervical cancer and improve overall health.
5. Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals, can support overall well-being and reduce the risk of cancer.
Cervical cancer is a preventable and treatable disease, yet it continues to pose a significant threat to women’s health worldwide. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures associated with cervical cancer, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their loved ones. Through vaccination, screening, and lifestyle modifications, we can work towards reducing the burden of cervical cancer and improving women’s health globally.
Cervical Cancer During Pregnancy: What You Need to Know
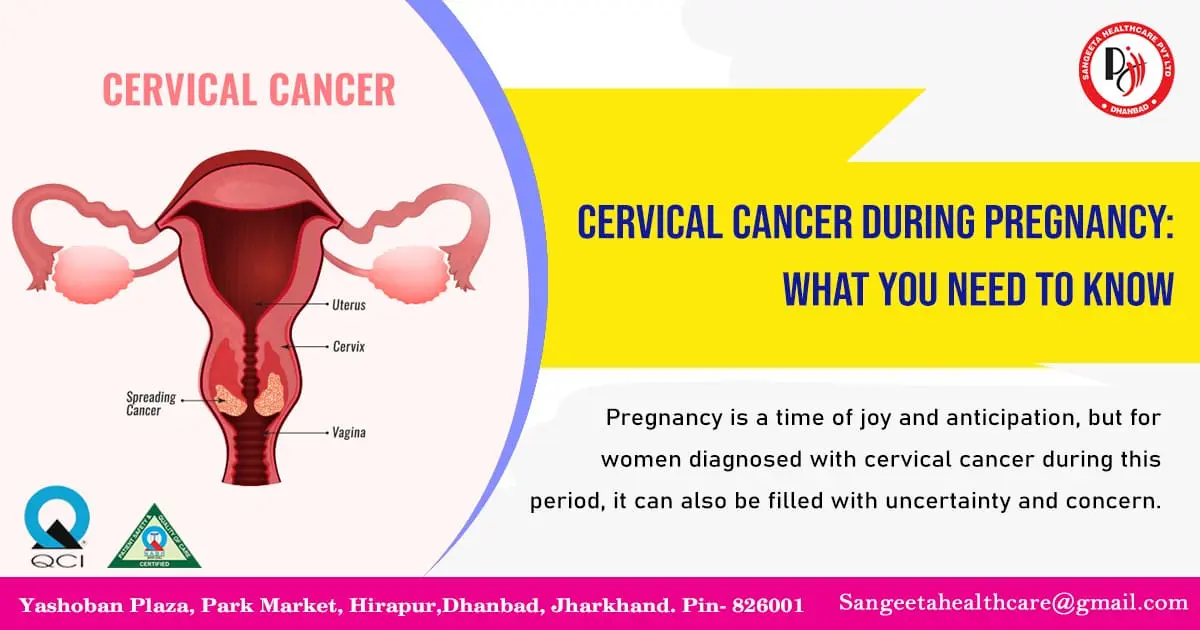
Pregnancy is a time of joy and anticipation, but for women diagnosed with cervical cancer during this period, it can also be filled with uncertainty and concern. Cervical cancer during pregnancy presents unique challenges, requiring careful management to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. In this blog post, we will explore the complexities of cervical cancer during pregnancy, including its diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of multidisciplinary care.
Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer during Pregnancy:
Diagnosing cervical cancer during pregnancy can be challenging due to the limitations of certain diagnostic procedures, such as biopsies and imaging tests, which may pose risks to the developing foetus. However, if a woman experiences abnormal symptoms or Pap smear results during pregnancy, further evaluation is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Understanding Cervical Cancer Symptoms during Pregnancy:
Cervical cancer may present with various symptoms, although it’s important to note that some women may not experience any symptoms at all, especially in the early stages of the disease. However, pregnant women should be vigilant about the following signs:
1. Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: One of the most common indications of cervical malignancy is unusual vaginal bleeding. This could include bleeding following menopause, after sexual activity, or in between cycles. Pregnant women experiencing any form of vaginal bleeding should promptly consult their healthcare provider for evaluation.
2. Increased Vaginal Discharge: Cervical cancer can cause changes in vaginal discharge, including an increase in volume or a change in consistency. Discharge may become watery, bloody, or have a foul odor. While some changes in discharge are normal during pregnancy, any unusual or persistent discharge should be reported to a healthcare professional.
3. Pelvic Pain or Discomfort: Pregnant women with cervical cancer may experience pelvic pain or discomfort, which can range from mild to severe. This pain could be ongoing or sporadic, and it might get worse with time. It is essential to distinguish between normal pregnancy discomfort and pain that may be indicative of an underlying health issue.
4. Pain during Intercourse: Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia) can be a symptom of cervical cancer. This pain may be due to changes in the cervix or surrounding tissues caused by the presence of cancerous cells.
Importance of Seeking Medical Attention:
Pregnancy can mask or mimic some symptoms of cervical cancer, making diagnosis more challenging. However, any unusual or persistent symptoms should not be ignored. Pregnant women who experience symptoms such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, changes in vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, or pain during intercourse should promptly inform their healthcare provider. Early detection and treatment of cervical cancer can significantly improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby, underscoring the importance of proactive healthcare during pregnancy.
It’s crucial for pregnant women to receive appropriate medical evaluation and diagnostic testing to rule out or confirm the presence of cervical cancer. Diagnostic procedures such as Pap smears, colposcopy, and biopsies may be performed as deemed safe and necessary by healthcare professionals.
Treatment Considerations:
The treatment of cervical cancer during pregnancy depends on several factors, including the stage of cancer, the gestational age of the fetus, and the mother’s overall health. Treatment options may include:
1. Monitoring: In cases where cervical cancer is detected in the early stages of pregnancy and the tumor is small, close monitoring may be recommended until after delivery.
2. Surgery: Depending on the stage of cancer and the gestational age of the fetus, surgery to remove the cancerous tissue may be an option. However, surgical interventions during pregnancy carry risks and must be carefully considered in consultation with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers.
3. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is generally not recommended during pregnancy due to the potential harm it can cause to the developing fetus. However, in certain cases where the benefits outweigh the risks, radiation therapy may be considered after the first trimester.
4. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is another treatment option for cervical cancer, but its use during pregnancy is limited due to concerns about its potential effects on the fetus. Chemotherapy is typically avoided during the first trimester and may be considered in later stages of pregnancy if necessary.
Multidisciplinary Care and Support:

Managing cervical cancer during pregnancy requires a coordinated approach involving obstetricians, oncologists, radiation oncologists, and other specialists. This multidisciplinary team works together to develop a personalized treatment plan that prioritizes the health and safety of both the mother and the baby.
In addition to medical care, emotional support and counseling are essential for women facing cervical cancer during pregnancy. Coping with a cancer diagnosis while pregnant can be overwhelming, and having access to supportive resources can help women navigate this challenging journey with confidence and resilience.
Cervical cancer during pregnancy presents unique challenges that require careful consideration and expert management. Cervical cancer during pregnancy is a rare but serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. While some symptoms of cervical cancer may overlap with normal pregnancy changes, it’s essential for expectant mothers to be aware of any unusual or persistent symptoms and to seek medical evaluation if concerns arise. With advances in medical technology and a multidisciplinary approach to care, women diagnosed with cervical cancer during pregnancy can receive treatment while safeguarding the health and well-being of themselves and their babies. By working closely with a team of healthcare professionals and accessing supportive resources, women can approach this journey with strength, hope, and optimism for the future.


