Kidneys are remarkable organs, silently working to filter waste, balance fluids, and regulate vital processes in your body. But what occurs when they begin to stumble? Kidney failure is a serious condition that affects millions worldwide, and its impact can range from manageable to life-threatening. Whether you’re a curious reader, a concerned individual, or a medical professional seeking a refresher, this guide dives deep into everything you need to know about kidney failure—its causes, symptoms, stages, diagnosis, treatment, and even how to prevent it. Let’s explore this critical health topic step by step.
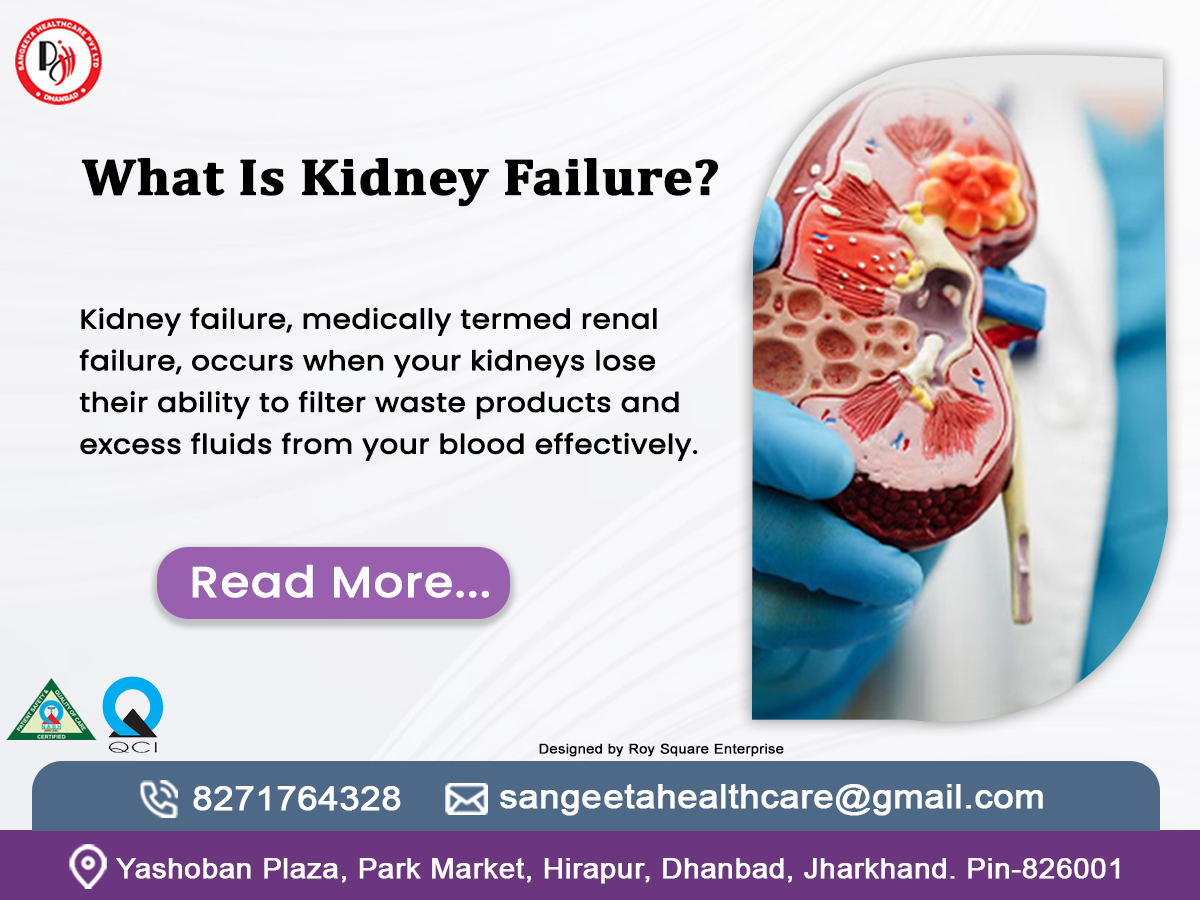
What Is Kidney Failure?
Kidney failure, medically termed renal failure, occurs when your kidneys lose their ability to filter waste products and excess fluids from your blood effectively. This condition doesn’t happen overnight—it can develop suddenly (acute kidney failure) or progressively over time (chronic kidney failure). When the kidneys fail, harmful toxins build up in the body, disrupting everything from blood pressure to red blood cell production.
There are two main types:
Acute Kidney Failure (AKF): A rapid decline in kidney function, often reversible with prompt treatment. It might stem from severe dehydration, injury, or medication side effects.
Chronic Kidney Failure (CKF): A gradual loss of kidney function over months or years, often linked to conditions like diabetes or hypertension. This type is typically irreversible without intervention.
Knowing what kidney failure means is key to understanding how serious it can be.It’s not just a standalone issue—it’s a signal that your body’s filtration system is in distress, and timely action can make all the difference.
What Are the Symptoms of Kidney Problems?
Kidney issues often creep up silently, especially in the early stages. Many people don’t realize there’s a problem until significant damage has occurred. So, what are the symptoms of kidney problems to watch for? Here’s a breakdown:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Reduced kidney function impairs red blood cell production, leading to anemia and exhaustion.
- Swelling (Edema): Swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or face happens due to the body holding onto extra fluid.
- Changes in Urination: You might notice foamy urine (proteinuria), blood in the urine (hematuria), or a decrease/increase in frequency.
- Shortness of Breath: When liquid collects in the lungs, it can make it hard to breathe.
- High Blood Pressure: Damaged kidneys struggle to regulate blood pressure, creating a vicious cycle.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Toxin accumulation can upset your stomach.
- Itchy Skin: Waste buildup in the blood can cause persistent itching.
For medicos, terms like oliguria (low urine output) or azotemia (elevated blood urea nitrogen) might come to mind as clinical indicators. For the general public, these symptoms might seem vague or unrelated at first, which is why awareness is key. If you’re experiencing a combination of these signs, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider—perhaps even a *chronic kidney disease specialist*—to investigate further.
Stages of Kidney Failure: A Progressive Journey
Kidney failure doesn’t strike all at once in chronic cases—it progresses through distinct phases known as the stages of kidney failure. These stages are defined by the Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), a measure of how well your kidneys filter blood. Let’s break them down:
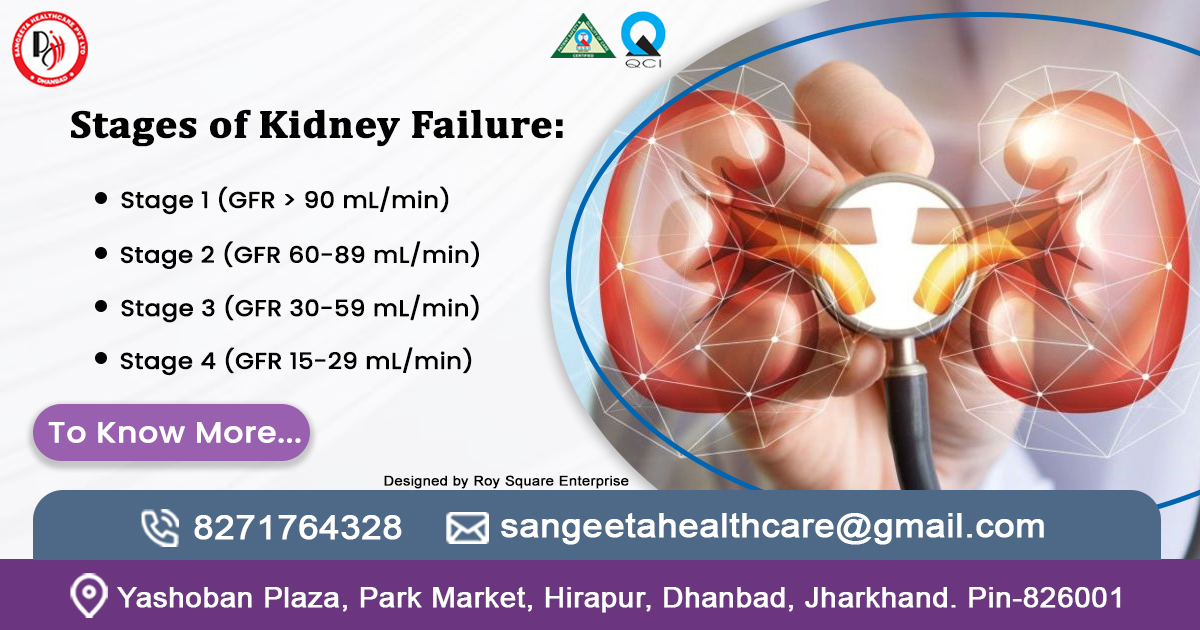
- Stage 1 (GFR > 90 mL/min): Kidney damage is present (e.g., protein in urine), but function remains normal. Symptoms are rare.
- Stage 2 (GFR 60-89 mL/min): Mild loss of function. Most people still feel fine, but underlying issues like hypertension may emerge.
- Stage 3 (GFR 30-59 mL/min): Moderate decline, split into 3a (45-59) and 3b (30-44). Fatigue, swelling, and urinary changes may appear.
- Stage 4 (GFR 15-29 mL/min): Severe reduction. Symptoms intensify, and preparation for dialysis or transplant may begin.
- Stage 5 (GFR < 15 mL/min): Final-stage kidney failure (ESRD).Kidneys are near total failure, requiring dialysis or transplant to survive.
For medical professionals, these stages guide treatment plans. For the average person, knowing the stages of kidney failure highlights why early detection matters. Progression isn’t inevitable—lifestyle changes and medical intervention can slow it down, especially in stages 1-3.
How Is Kidney Failure Diagnosed?
Wondering “how is kidney failure diagnosed?” It’s a multi-step process that combines clinical evaluation with precise tests. Here’s how doctors pinpoint the problem:
Blood Tests:
- Serum Creatinine: Elevated levels indicate poor kidney filtration.
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): High BUN reflects waste buildup.
- GFR Calculation: Derived from creatinine, age, sex, and race, this is the gold standard for assessing kidney function.
Urine Tests:
- Urinalysis: Checks for protein, blood, or glucose in the urine.
- Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (ACR): Detects early kidney damage through protein levels.
Imaging:
- Ultrasound: Visualizes kidney size, structure, or blockages.
- CT Scan: Identifies stones, tumors, or abnormalities.
- Biopsy: In complex cases, a small kidney tissue sample is analyzed for specific diseases (e.g., glomerulonephritis).
A chronic kidney disease specialist, or nephrologist, often oversees this process, especially for chronic cases. For the general public, the takeaway is simple: routine checkups can catch kidney issues early, even if you feel fine. Don’t wait for symptoms to escalate—proactive testing saves lives.
Treatment of Kidney Failure: Options and Hope
When it comes to the treatment of kidney failure.The approach depends on whether it’s acute or chronic, and the stage of progression. Here’s a comprehensive look:
Acute Kidney Failure:
Fluid Management: IV fluids for dehydration or diuretics to remove excess fluid.
Medication Adjustments: Stopping nephrotoxic drugs (e.g., NSAIDs).
Addressing the Cause: Treating infections, removing blockages, or stabilizing blood loss.
Chronic Kidney Failure:
Medications: ACE inhibitors for blood pressure, erythropoietin for anemia, or phosphate binders for mineral balance.
Dialysis:
Hemodialysis: Blood is filtered through a machine (3-4 times weekly).
Peritoneal Dialysis: Uses the abdominal lining to filter waste daily.
Kidney Transplant: Replacing the failed kidney with a donor organ—often the best long-term solution.
Supportive Care: Diet changes (low sodium, potassium, and protein), exercise, and quitting smoking can ease the burden on kidneys.
Consulting a chronic kidney disease specialist ensures a tailored plan. For patients, these treatments offer hope—dialysis and transplants have transformed ESRD from a death sentence to a manageable condition. The key? Early intervention and adherence to medical advice.
How to Prevent Kidney Failure: Take Charge of Your Health
Prevention is powerful, and how to prevent kidney failure is a question worth exploring. Here are actionable steps:

- Manage Chronic Conditions: Keep diabetes and hypertension in check with regular monitoring and medication.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake supports kidney function (aim for 8-10 cups daily, unless restricted).
- Healthy Diet: Reduce salt, processed foods, and excess protein; opt for fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit alcohol, quit smoking, and use medications only as prescribed.
- Exercise Regularly: 30 minutes most days boosts circulation and kidney health.
- Routine Checkups: Annual blood and urine tests catch issues early.
For medicos, emphasizing patient education on modifiable risk factors is crucial. For everyone else, these habits aren’t just about kidney health—they enhance overall well-being
Why Consult a Chronic Kidney Disease Specialist?
A chronic kidney disease specialist (nephrologist) brings expertise that general practitioners may not have. They interpret complex test results, recommend advanced treatments, and coordinate care for dialysis or transplant. If you’re at risk—due to family history, diabetes, or persistent symptoms—seeing a specialist early can slow progression and improve outcomes. Think of them as your kidney’s best advocate.
Take Control of Your Kidney Health Today
Your kidneys play a vital role in your well-being, and now that you’re equipped with the knowledge—from understanding what kidney failure is to exploring prevention strategies—it’s time to act. Don’t wait for symptoms to dictate your next step. Schedule a routine checkup with your healthcare provider to monitor your kidney function, or consult a chronic kidney disease specialist if you’re at risk. Small changes, like adopting a kidney-friendly diet or managing chronic conditions, can go a long way. Share this guide with loved ones to spread awareness, and let’s work together to protect our health. Take the first step now—your kidneys will thank you.
Here are some FAQs :
- What Exactly Is Kidney Failure?
Kidney failure happens when your kidneys can’t filter waste and fluids from your blood like they should. Think of them as your body’s cleanup crew—if they go on strike, toxins pile up, and trouble starts. It can hit suddenly (acutely) due to an injury or illness, or creep up over time (chronic) from things like diabetes. Either way, it’s serious—but with the right care, it’s manageable.
- What Are the Main Symptoms of Kidney Problems?
Your kidneys are quiet workers, so early signs can be sneaky. Look out for tiredness, swollen legs or feet, weird changes in your pee (like foam or blood), shortness of breath, or itchy skin that won’t quit. Feeling queasy or noticing your blood pressure spiking? That could be a clue too. If these sound familiar, don’t brush them off—check in with a doctor.
- Can Kidney Failure Be Cured?
Here’s the honest scoop: acute kidney failure can sometimes bounce back with quick treatment, like fixing dehydration or an infection. Chronic kidney failure, though, is trickier—it’s usually a one-way street unless you get a transplant. But don’t lose hope! Treatments like dialysis keep people thriving, and early action can slow it down big time.
- What Causes Kidney Failure?
Lots of culprits can crash your kidneys. For acute cases, think of severe infections, dehydration, or meds that stress them out (like too many painkillers). Chronic failure often ties back to diabetes, high blood pressure, or diseases like polycystic kidney disease. Bad habits—smoking, poor diet—don’t help either. It’s like a perfect storm when risks stack up!
- How Do Doctors Diagnose Kidney Failure?
Doctors play detective with a few key tools. They’ll test your blood for creatinine (a waste marker) and calculate your GFR (a score of how well your kidneys filter). Urine tests check for protein or blood, while scans like ultrasounds peek at your kidneys’ shape. Sometimes, they even snag a tiny tissue sample. It’s a team effort to crack the case!
- What Are the Stages of Kidney Failure?
Chronic kidney failure rolls out in five stages, based on how well your kidneys filter (GFR). Stage 1 is mild—damage is there, but you feel okay. By Stage 3, you might notice symptoms like swelling. Stage 5 is the endgame—your kidneys are barely hanging on, and you’ll need dialysis or a transplant. Catching it early can change the story!
- What’s the Best Treatment for Kidney Failure?
Treatment depends on the type. Acute failure might just need fluids or meds to fix the root issue. For chronic cases, you’ve got options: dialysis cleans your blood artificially (think of it as a kidney stand-in), or a transplant gives you a fresh start with a donor kidney. Meds, diet tweaks, and lifestyle shifts back it all up. A specialist can map out what’s best for you.
- Can I Prevent Kidney Failure?
Absolutely, and it’s easier than you think! Keep diabetes and blood pressure in check, drink plenty of water, and eat smart—less salt, more veggies. Skip the smoking, go easy on booze, and move your body regularly. Routine checkups spot trouble early. It’s like giving your kidneys a VIP protection plan!
- How Does Dialysis Work, and Is It Painful?
Dialysis is like a superhero sub for your kidneys. In hemodialysis, a machine filters your blood a few times a week—no pain, just some discomfort from the needles. Peritoneal dialysis uses your belly lining to clean blood daily, with a tube that might feel odd at first. It’s not a picnic, but it’s a lifesaver, and people get used to it.
- When Should I See a Chronic Kidney Disease Specialist?
If you’ve got risk factors—like a family history, diabetes, or funky symptoms—don’t wait. A chronic kidney disease specialist (nephrologist) is your go-to for expert care. They’re pros at reading tricky test results, slowing damage, and planning big moves like dialysis. Think of them as your kidney’s personal coach—get them on speed dial if things feel off!