Some facts about Uterine Fibroids you should know

Many women are suffering because of Uterine Fibroids. It generally develops in a woman’s reproductive years. Uterine fibroids are a kind of tumor that grows in the wall of the uterus. Fibroids are normally non-cancerous. They can differ in size. But if you ignore the treatment you may face other health-related issues like abdominal pain, pregnancy issues and many. So, it’s better to receive early diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Normal fibroids generally don’t show any symptoms but in severe cases symptoms of uterine fibroids are
- Heavy bleeding in your period
- Pelvic pain
- Pain in lower abdomen
- Painful intercourse
- Constipation
- Back pain
- Weight changes
- Anemia
- Fatigue
Types of Uterine Fibroid
On the basis of the location of fibroids in the uterus, we generalized them into four types. The types of uterine fibroids are:
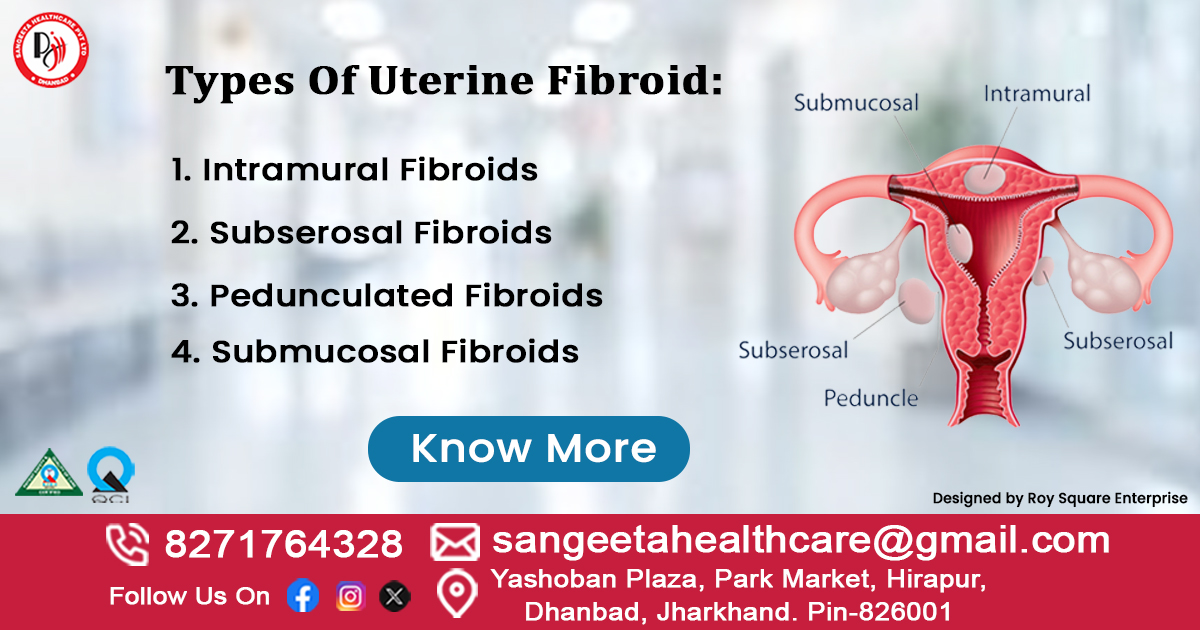
- Intramural Fibroids: These fibroids grow within the uterine wall, making them the most common type. While typically harmless, they can cause issues like heavy bleeding, painful sex, back pain, and fertility challenges.
- Subserosal Fibroids: Growing outside the uterus, these fibroids can become large and lead to complications. Small ones might not cause severe symptoms but can lead to back pain or bladder pressure.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: Attached to the uterus by a stalk-like growth, these fibroids can grow inside or outside the uterus. When inside, they’re called pedunculated submucosal fibroids.
- Submucosal Fibroids: Developing beneath the uterine lining, these non-cancerous fibroids can vary in size. They can cause complications during fertility processes and lead to heavy bleeding or prolonged periods.
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids can be so tiny that you need a microscope to see them, also, sometimes they grow very large. The exact cause of getting them is not clear, but here are some suspected facts mentioned below:
- Hormonal fact: Estrogen and progesterone are the two hormones, that are responsible for thickening the uterus lining during each menstrual to prepare it for pregnancy. These hormones also help to grow fibroids. Fibroids have more cells that respond to estrogen and progesterone than normal uterine cells. That’s why fibroids start to shrink after menopause because of low hormone levels.
- Family history: Women who have a family history of this disease, have a higher risk of developing it. Genetic mutations can develop fibroids.
Risk factors of Uterine Fibroids
Women of reproductive are have higher risk. Other risk factors related to uterine fibroids are
- Age: Though fibroids can come at any age but it is common when you get older. Women may face this in their late 30’s or early 40’s until menopause. After menopause, the fibroids started to shrink on their own.
- Obesity: A higher body mass index (BMI) is associated with the risk of uterine fibroids. Fat cells produce estrogen and when estrogen and progesterone levels are high, they increase the risk of obesity.
- Early onset of menstruation: Research suggests that women who start menstruating at a younger age are more likely to develop fibroids. Generally, girls experience their first period around 12-13 years old. However, studies have found that early menstruation is associated with a higher risk of fibroids.
Diagnosis of Uterine Fibroids
To diagnose fibroids, your doctor may recommend a few tests, so that they can properly get the details and proceed for further treatment.

- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the uterus.
- MRI: It uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of the uterus.
- Saline Infusion Sonogram (Hysterosonography): Involves injecting saline into the uterus to enhance ultrasound imaging.
- Hysteroscopy: Uses a thin, flexible tube inserted through the vagina to visually examine the inside of the uterus.
- Laparoscopy: Here a thin telescope is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen to check your reproductive organs.
How Uterine Fibroids are treated?
The treatment of uterine fibroids depends on various factors, like your age, your concern, whether you are pregnant or not, your fibroid size, your health issues & many others. Generally, fibroids don’t need treatment, but if they become severe then they require treatment.
- Medications and hormonal therapies: To reduce the symptoms of fibroids doctors will use intrauterine devices. It will help to help to release hormones to overcome the heavy bleeding & pain. Doctors may prescribe iron supplements in case you have anemia due to heavy bleeding. To give you relief from period cramps they will also suggest pain relievers, like ibufrofen or naproxen. By stopping the ovulation process hormonal shots can be taken to shrink the fibroids.
- Dietary changes: Dietary changes can help a lot prevent fibroids or manage them. Fruits, vegetables, vitamin D, Omega3 fatty acids and fiber should be in your diet.
- Other processes: Avoid processed foods, don’t drink alcohol, quit smoking, regular exercise, and weight maintenance can help.
Surgical Procedures
If medications and hormonal therapies don’t work, doctors may suggest you surgeries to remove fibroids. Surgical procedures include:
- Endometrial Ablation: This minimally invasive procedure uses high-energy heat to destroy the uterine lining, effectively treating small fibroids.
- Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): In this procedure, tiny particles are injected into the uterine arteries, blocking blood flow to the fibroids and causing them to shrink.
- Myomectomy: This surgical procedure removes fibroids while preserving the uterus, making it a suitable option for women who wish to become pregnant in the future.
- Hysterectomy: This surgical procedure involves the removal of the entire uterus and is typically recommended for women who no longer wish to become pregnant. The concept of surgery is different from myomectomy.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
- What is uterine fibroids?
Answer: Fibroids are like, that grows in uterus. And it’s noncancerous.
- What are the symptoms of uterine fibroids?
Answer: Heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, lower abdomen pain, painful intercourse, constipation are the common signs of uterine fibroids.
- What are the risk factors of uterine fibroids?
Answer: Obesity, age, early onset of menstruation can be risky for uterine fibroids.
- What are the surgical options for uterine fibroids?
Answer: Endometrial ablation, Uterine artery, Embolization, Myomectomy, and Hysterectomy are the surgical options for uterine fibroids.


